

Anatomical dead space occurs naturally in areas of the lungs that don’t come in contact with alveoli (like the trachea).

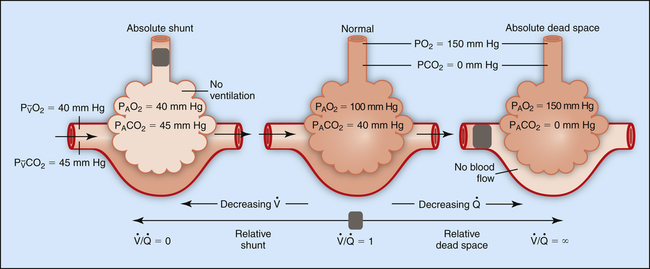
This difference between the amounts of air and blood reaching the lungs is referred to as ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) mismatch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
